Introducing the Equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s Principle Worksheet Answers, an authoritative resource designed to empower students and practitioners alike with a thorough understanding of this fundamental concept in chemistry. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of chemical equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s principle, providing a clear and systematic approach to solving complex problems.
Through a series of engaging and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet challenges readers to apply their knowledge of equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s principle to real-world scenarios. Each question is carefully crafted to reinforce key concepts and foster a deeper comprehension of the material.
Equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s Principle: Equilibrium And Le Chatelier’s Principle Worksheet Answers
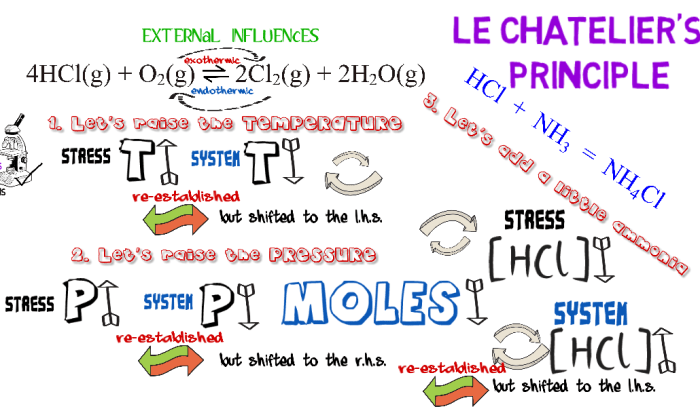
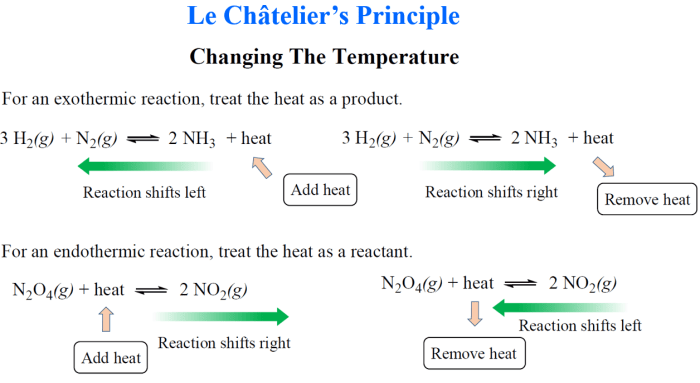
Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction do not change over time. Le Chatelier’s principle is a useful tool for predicting how chemical equilibrium will shift when the conditions of the reaction are changed.
Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
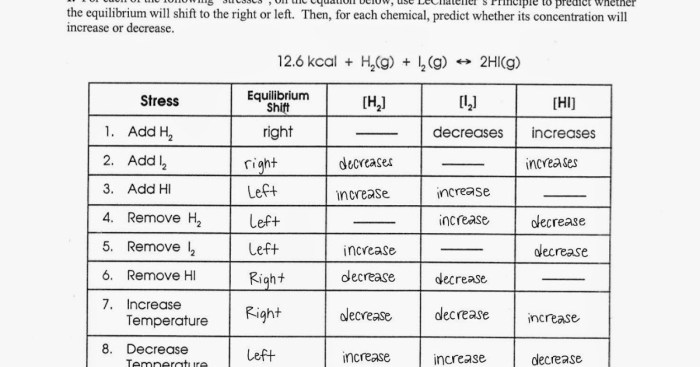
- Temperature:Increasing the temperature of a reaction will shift the equilibrium towards the endothermic side (the side that absorbs heat).
- Pressure:Increasing the pressure of a reaction will shift the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas.
- Concentration:Increasing the concentration of a reactant will shift the equilibrium towards the product side, while increasing the concentration of a product will shift the equilibrium towards the reactant side.
Le Chatelier’s Principle Worksheet
Question 1:A reaction between hydrogen and iodine to form hydrogen iodide is exothermic. How will the equilibrium shift if the temperature is increased?
Answer:According to Le Chatelier’s principle, increasing the temperature will shift the equilibrium towards the endothermic side, which is the side that absorbs heat. Therefore, the equilibrium will shift towards the formation of hydrogen iodide.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Question 2: A reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen to form ammonia is carried out in a closed container. How will the equilibrium shift if the volume of the container is decreased? | Answer: Decreasing the volume of the container will increase the pressure. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the equilibrium will shift towards the side with fewer moles of gas. Therefore, the equilibrium will shift towards the formation of ammonia. |
| Question 3: A reaction between carbon monoxide and oxygen to form carbon dioxide is at equilibrium. How will the equilibrium shift if carbon monoxide is added to the reaction? | Answer: Adding carbon monoxide to the reaction will increase its concentration. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the equilibrium will shift towards the product side, which is the side that consumes carbon monoxide. Therefore, the equilibrium will shift towards the formation of carbon dioxide. |
Equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s Principle Applications
Equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s principle have numerous applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Predicting the behavior of chemical reactions and optimizing reaction conditions.
- Biology:Understanding biochemical reactions and maintaining homeostasis in living organisms.
- Environmental science:Predicting the behavior of pollutants and developing strategies for pollution control.
For example, Le Chatelier’s principle can be used to predict the effect of adding a buffer to an acidic solution. A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH by absorbing or releasing hydrogen ions. When a buffer is added to an acidic solution, the equilibrium between the hydrogen ions and the buffer will shift towards the formation of the buffer, thereby neutralizing the acid.
Advanced Equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s Principle, Equilibrium and le chatelier’s principle worksheet answers
Advanced concepts related to equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s principle include:
- Heterogeneous equilibrium:Involving reactions between different phases, such as solid and gas.
- Equilibrium constant:A numerical value that describes the extent to which a reaction proceeds towards equilibrium.
Limitations of Le Chatelier’s principle include its inability to predict the direction of reactions that are not at equilibrium and its assumption that the system is closed and isolated.
FAQ Explained
What is chemical equilibrium?
Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction do not change over time.
What is Le Chatelier’s principle?
Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a change is made to a system in equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the change.
How can I use Le Chatelier’s principle to predict the behavior of chemical systems?
By applying Le Chatelier’s principle, you can predict how a chemical system will respond to changes in temperature, pressure, concentration, or the addition of a catalyst.