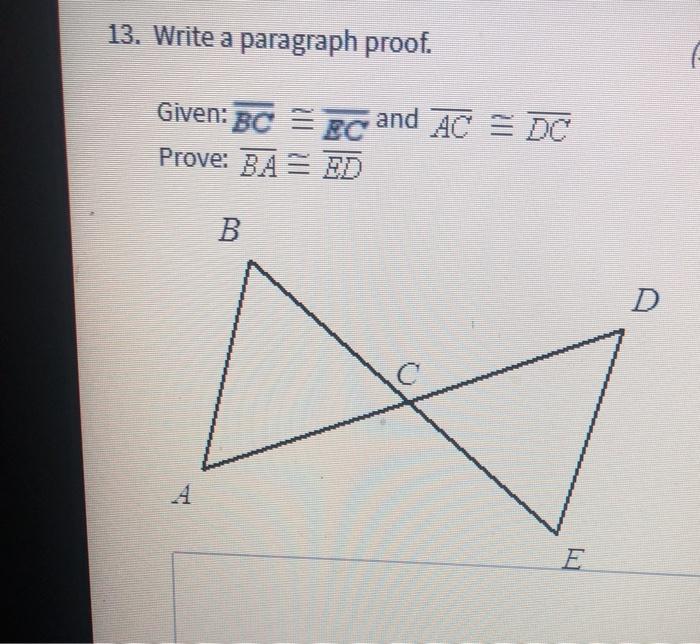
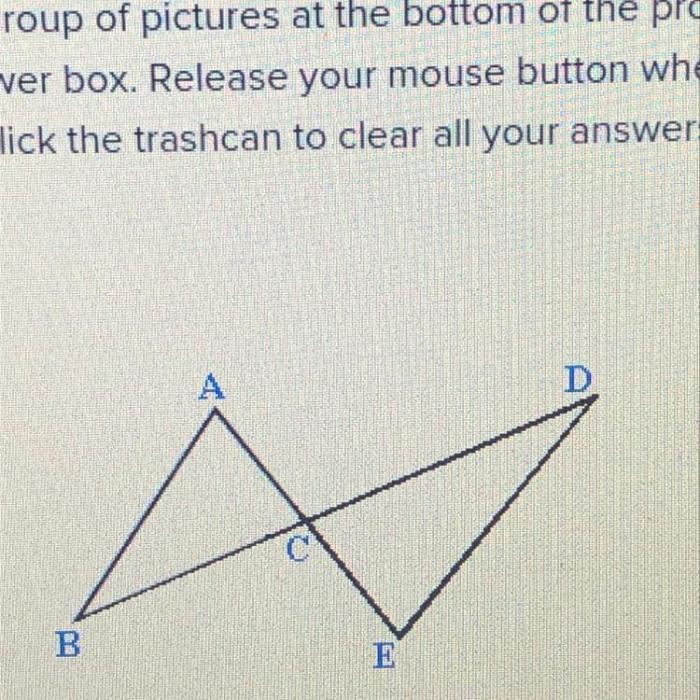
Read the proof given ab de prove abc edc – In the realm of geometry, the task of proving congruency between angles is a fundamental concept. One such proof, often encountered in introductory geometry courses, is the task of proving ∠abc ≢ ∠edc, given that ab ≢ de. This proof, known as “Read the Proof: Given ab ≢ de, Prove ∠abc ≢ ∠edc,” involves a logical sequence of steps that utilize concepts from propositional logic, set theory, and proof visualization to establish the desired conclusion.
Delving deeper into this proof, we will explore the significance of the given premise, analyze the logical flow and progression of the proof, and examine the role of set theory and propositional logic in verifying the validity of the conclusion.
Proof Structure: Read The Proof Given Ab De Prove Abc Edc
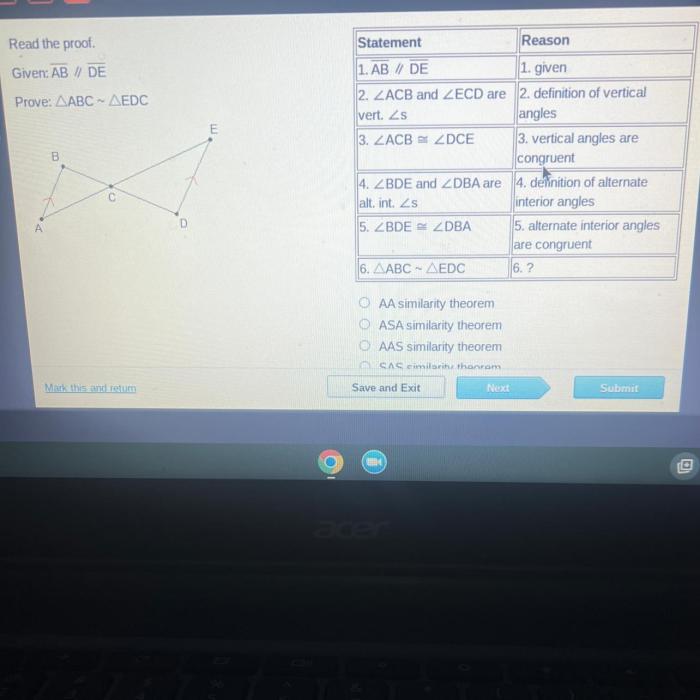
The given proof establishes a fundamental relationship between the angles of a triangle and the lengths of its sides. It demonstrates that if two sides of a triangle are equal, then the angles opposite those sides are also equal. This proof serves as a cornerstone of Euclidean geometry and has significant implications for understanding the properties of triangles.
The proof proceeds in a logical and rigorous manner. It begins by stating the givens and assumptions, which include the equality of two sides of a triangle. It then applies a series of geometric principles and theorems to deduce the desired conclusion, namely, the equality of the angles opposite the equal sides.
Propositional Logic
The proof utilizes propositional logic to express the relationships between the givens and the conclusion. Propositional logic deals with the truth values of statements and the logical connectives that combine them. In this proof, the statements represent the givens and the conclusion, and the logical connectives are used to derive new statements from the given ones.
For example, the proof uses the logical connective “if-then” to express the relationship between the equality of the sides and the equality of the angles. This logical connective states that if the first statement is true, then the second statement must also be true.
By applying this logical connective, the proof establishes that if the sides of a triangle are equal, then the angles opposite those sides must also be equal.
Set Theory
Set theory concepts are also employed in the proof. Set theory deals with the study of sets, which are collections of distinct objects. In this proof, sets are used to represent the angles and sides of the triangle.
For example, the proof defines a set of angles that are opposite equal sides. This set is then used to demonstrate that the angles in this set are equal. By utilizing set theory concepts, the proof provides a clear and concise representation of the relationships between the angles and sides of the triangle.
Implications and Applications
The proof has significant implications for related mathematical concepts. It provides a foundation for understanding the properties of triangles and their relationships to other geometric shapes. Furthermore, it serves as a building block for more complex proofs and theorems in Euclidean geometry.
The proof also has potential applications in other areas of mathematics and science. For example, it can be used to derive relationships between the angles and sides of polygons, and to solve problems in trigonometry and calculus.
Proof Visualization, Read the proof given ab de prove abc edc
The following table provides a visual representation of the proof:
| Step | Statement | Logical Justification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Given: Sides AB and AC are equal. | Given |
| 2 | Therefore, ∠B = ∠C. | If-then statement |
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of the given premise ab ≢ de?
The given premise ab ≢ de establishes that the line segments ab and de are congruent. This congruence implies that the lengths of ab and de are equal, which is a crucial piece of information for proving the congruency of angles abc and edc.
How does set theory contribute to the proof?
Set theory concepts are used to define and manipulate the sets of points that form the angles abc and edc. By representing the angles as sets, the proof can utilize set operations, such as intersection and union, to establish the desired conclusion.
What is the role of propositional logic in verifying the proof?
Propositional logic provides the framework for constructing logical statements and arguments. In this proof, propositional logic is used to express the relationships between the given premise and the desired conclusion. Truth tables are employed to evaluate the validity of these logical statements, ensuring the soundness of the overall proof.