The CPT code for dental implant is a crucial element in the billing and reimbursement process for this dental procedure. Understanding the code, its significance, and the factors that determine it is essential for dental professionals and patients alike. This article delves into the world of dental implant CPT codes, providing a comprehensive overview that will empower you with the knowledge you need.
Dental implants have revolutionized the field of dentistry, offering a permanent solution for missing teeth. The placement of a dental implant involves a surgical procedure that requires specialized training and expertise. The CPT code assigned to this procedure plays a vital role in determining the reimbursement rates and ensuring accurate billing.
Dental Implant Overview
Dental implants are a type of dental restoration that is used to replace missing teeth. They are made of titanium and are surgically placed into the jawbone. Dental implants are a permanent solution for missing teeth and can last for many years.Dental
implants have a number of benefits over other types of dental restorations, such as bridges or dentures. Dental implants are more stable and secure than other types of restorations, and they do not require the removal of healthy teeth. Dental implants also help to preserve the jawbone, which can prevent facial collapse.There
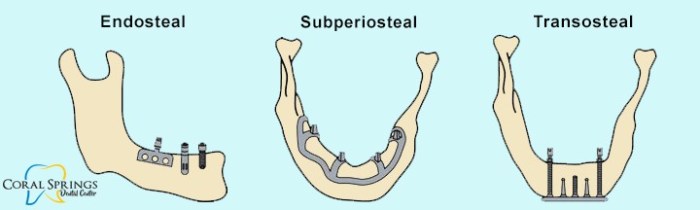
are two main types of dental implants: endosteal implants and subperiosteal implants. Endosteal implants are the most common type of implant. They are placed directly into the jawbone. Subperiosteal implants are placed on top of the jawbone.The procedure for placing a dental implant typically involves several steps.
If you’re looking for information on the CPT code for dental implants, consider checking out our comprehensive study guide available as a free PDF download. This guide covers everything you need to know about the CPT code for dental implants, including the specific codes to use and how to bill for them correctly.
Download the CPCE study guide today to enhance your understanding of the CPT code for dental implants and ensure accurate billing.
First, the dentist will make an incision in the gum tissue and expose the jawbone. Then, the dentist will drill a hole in the jawbone and place the implant. The implant will be allowed to heal for several months before the dentist places the abutment and crown.
CPT Code for Dental Implant
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code for a dental implant is 60100. This code represents the surgical placement of an implant into the jawbone to support a dental prosthesis, such as a crown, bridge, or denture.
Factors Determining CPT Code, Cpt code for dental implant
The specific CPT code used for a dental implant depends on several factors, including:
- Location of the implant:Implants placed in different areas of the jawbone (e.g., anterior, posterior) may have different CPT codes.
- Type of implant:Endosteal implants (placed within the jawbone) and subperiosteal implants (placed on top of the jawbone) have different CPT codes.
- Surgical approach:Open flap surgery (where the gum tissue is cut and lifted to expose the jawbone) and flapless surgery (where the implant is placed through a small hole in the gum tissue) have different CPT codes.
- Number of implants:The CPT code will vary depending on the number of implants being placed.
Billing and Reimbursement for Dental Implants
Dental implants are billed using specific Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes that describe the surgical procedure performed. The billing process involves submitting a claim to the patient’s insurance provider, which includes the CPT code, a description of the procedure, and the fee charged.Reimbursement
rates for dental implants vary depending on the insurance provider, the geographic location, and the complexity of the procedure. Generally, insurance companies reimburse a portion of the cost of the implant, but the patient is responsible for the remaining balance.Several
factors affect reimbursement for dental implants, including:
- The type of implant used (e.g., single-tooth implant, multiple-tooth implant)
- The location of the implant (e.g., upper jaw, lower jaw)
- The surgical complexity of the procedure
- The geographic location of the practice
It’s important to note that reimbursement rates for dental implants can change over time, so it’s essential to check with the insurance provider for the most up-to-date information.
Dental Insurance Coverage for Dental Implants
Dental insurance typically provides some coverage for dental implants, but the extent of coverage varies widely depending on the insurance plan. Some plans may cover a portion of the cost of the implant, while others may cover the entire cost.
It is important to check with your insurance provider to determine what coverage is available.
Limitations and Exclusions
There are often limitations and exclusions to dental insurance coverage for dental implants. For example, some plans may only cover implants that are placed to replace missing teeth due to an accident or disease. Other plans may exclude coverage for implants that are placed for cosmetic purposes.
It is important to read your insurance policy carefully to understand what is and is not covered.
Tips for Maximizing Coverage
There are a few things you can do to maximize your dental insurance coverage for dental implants:
- Choose a dental insurance plan that offers good coverage for dental implants.
- Get pre-approval from your insurance provider before having the implant placed.
- Provide your insurance provider with all of the necessary documentation, such as a treatment plan and x-rays.
- Be prepared to pay a portion of the cost of the implant out-of-pocket.
Patient Education on Dental Implants
Dental implants are a popular and effective way to replace missing teeth. They are made of titanium, a biocompatible material that fuses with the jawbone over time. This provides a strong and stable foundation for the implant, which can then be used to support a crown, bridge, or denture.
Dental implants offer several benefits over other tooth replacement options, including:
- They look and feel like natural teeth.
- They are durable and can last for many years.
- They do not require special care, beyond regular brushing and flossing.
- They can improve oral health by preventing bone loss and gum disease.
However, dental implants also have some risks, including:
- They can be expensive.
- They require surgery to place.
- They can sometimes fail, requiring additional treatment.
The cost of dental implants varies depending on the number of implants needed, the type of implant used, and the location of the implant. The average cost of a single implant is between $3,000 and $5,000.
Dental implants are a good option for people who are missing teeth and want a long-lasting, natural-looking solution. However, it is important to be aware of the benefits and risks of dental implants before making a decision.
How to Care for Dental Implants
Caring for dental implants is important to ensure their longevity and success. Here are some tips on how to care for your dental implants:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss your teeth once a day with unwaxed dental floss.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Avoid chewing on hard foods or objects, such as ice or candy.
- See your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
Top FAQs
What is the CPT code for a dental implant?
The CPT code for a dental implant is D6060.
What does the CPT code for a dental implant include?
The CPT code for a dental implant includes the surgical placement of the implant fixture, the abutment, and the crown.
What factors affect the CPT code for a dental implant?
The factors that affect the CPT code for a dental implant include the type of implant, the location of the implant, and the complexity of the procedure.